 |
 |
- Search
| J Neurointensive Care > Volume 1(1); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the factors that influence the determination of treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs), we retrospectively compared various well-known risk factors that are associated with future rupture for treated and observed groups.
Methods
Between January 2006 and December 2016, a total of 279 patients treated UIAs with surgical clipping or coil embolization have been included in this study. In the same period, 100 patients did undergo transfemoral cerebral angiograms and were initially managed with observation. Aneurysmal characteristics and patinets were compared between the treated and the observed group. The association between these factors and the decision of treatment was performed using a multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
279 patients with treated unruptured aneurysms and the observation group included 100 patients with unruptured aneurysms. A multivariate study revealed that young age (OR=0.959 / p=0.001), high aneurysms height, (OR=1.906 / p=0.002), daughter sac (OR=4.072 / p=0.001), location of aneurysms (anterior communicating artery (OR=3.729 / p=0.022) and middle cerebral artery bifurcation (OR=4.110 / p=0.009) were significantly associated with the treatment group when compared to the observation group.
Autopsy studies have shown an occurrence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) incidences in approximately 5 percent of all performed autopsies6,13). 6 of 100,000 patients will have ruptured aneurysm induced subarachnoid hemorrhage each year in the USA1,17). UIAs are a cerebrovascular condition that are commonly diagnosed due to improved imaging techniques. While the rupture risk of UIAs leads many neurosurgeons to advise its preventive treatment, the management of patients with UIAs remains controversial. Surgeon preference and experience as well as morphologic and anatomic considerations play important roles in the debates that continue over the controversy about whether to treat UIAs. Many studies have reported that certain patient characteristics increase the risk of rupture, including old age, female gender, and Japanese or Finnish descent. Aneurysms characteristics that increase the risk of rupture are location at the posterior circulation and increasing size10,22,32,33). Thus, these factors affect the management of UIAs. In this study, we evaluated the association between these risk factors, which are involved in future rupture of UIAs and management decision.
The treatment group included a total of 279 patients with UIAs and who were treated with surgical clipping or coil embolization between January 2006 and December 2016. In the same period, 100 patients who underwent transfemoral cerebral angiography (TFCA) and who were initially managed with observation were included in the observation group. Patients with UIAs who did not undergo TFCA were excluded16). Patients were also excluded if they had any of 1) Prior SAH, 2) symptomatic aneurysm, and 3) fusiform aneurysm. Clinical outcomes, aneurysmal characteristics (location, size, and morphological characteristics of lesions) and clinical presentation parameters, underlying disease were evaluated for both groups.
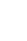
All UIAs were classified into the following categories based on location: 1. middle cerebral artery (MCA), 2. anterior communicating artery (ACoA) including distal anterior cerebral artery, 3. cavernous ICA, 4. internal carotid artery (ICA), 5. posterior communicating artery (PCoA), 6. Basilar top, and 7. vertebrobasilar artery (VBA). ICA included the location between the cavernous portion of ICA and the internal carotid artery bifurcation and the origin of the anterior choroidal artery, excluding those located at the origin of the posterior communicating. Aneurysmal factors included height, neck and width of aneurysm, which were measured via TFCA images. The maximum diameter was defined as the longest diameter of UIA. Aspect ratio means the ratio of height to neck (Fig. 1).
The following factors of the patients with aneurysms, whether treated or not, were collected and analyzed to examine their relationships with treatment indication. Included patient factors were age, sex, underlying disease: hypertension (previously known, patient being treated with antihypertensive medications, or blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg during the nonacute phase), and diabetes mellitus (DM) (fasting glucose > 7 mmol/L or patient being treated with antidiabetic medication), smoking history
(current or past), alcohol history, and other diseases, such as history of ischemic stroke or cardiac disease (heart failure, arrhythmia). 18 patients of the treated group had multiple aneurysms (6.4%) and 7 patients of the observation group had multiplicity (7%). The total number of treated aneurysms was 297 and 108 aneurysms were observed.
After patients were diagnosed with UIA through CT angiography or MR angiography, they were admitted and underwent the TFCA. Based on the results, medical staff (neurosurgeon and neuroradiologist) consulted with the patients and their caregivers to determine a treatment plan.
The methods of operation mean surgical clipping and endovascular treatment included coil embolization and stent assisted coiling26).
In the treated group, the outcome of each patient was assessed using the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) 1 month after the operation day. A Glasgow Outcome score of 5 indicates no disability, a score of 4 or 3 indicates both moderate disability, i.e., no need for assistance in everyday life, employment is possible but may require special equipment, and severe disability, i.e., severe injury with permanent need for help with daily living, a score of 1 to 2 indicates death or a persistent vegetative state. The mean follow up duration for the observation group was 33.66 month.
A statistical analysis was performed via binary logistic regression to analyze any independent association between the groups, and odds ratio (ORs) and their 95% confidence interval (CIs) were estimated. Both multivariate and univariate analysis were performed. The data are expressed as a mean ± standard deviation (SD). p-values of less than 0.05 (p<0.05) were considered statistically significant. Between-cohort comparisons of the distributions of baseline characteristics were done with the Chi-squared test for categorical variables and with the Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables. Analyses were performed with SPSS ver. 23.0 (IBM corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Table 1 showed the comparison of patient and aneurysmal characteristics between the treated and observation groups.
A total of 279 patients with newly diagnosed aneurysms that underwent treatment for aneurysms were reviewed over a period of 10 years. The group included 84 men (31%) and 195 women (69%) with an average age of 58.49 years (± 10.71). The observation group consisted of 27 men (27%) and 73 women (73%) with an average of 61.9 years (± 11.11). Both groups together included 77 patients who were older than 70 years (19%). Age and smoke history were statistically association in comparison between treated and observation group (p=0.007 and 0.011, respectively). 268 patients had female gender, 216 patients had hypertension and 41 patients had diabetes mellitus, however their distribution between treated group and observation group was not statistically significant (p=0.610 for sex, p=0.242 for hypertension and p=0.708 for diabetes mellitus). The number of patients who with a history of drinking alcohol showed no difference between two groups (p=0.893).
160 patients underwent surgical clipping and 119 patients underwent endovascular treatment. Mean neck size which was 3.60±1.51 in treated group, was not significant higher than the 3.34±1.78 of the observation group (p=0.153). However mean height was significantly different (5.13±3.39 in treated grup and 3.37±3.30 in observation group, p=0.001). The height of aneurysms was bigger than 5 mm in 94 patients. The mean width was also statistically higher in treated group (5.62±5.09) than observation group (4.08±3.77) (p=0.006). The maximum diameter (6.27±5.26 in treated group and 4.27±4.04 in observation group) and aspect ratio (1.46±0.79 in treated group and 1.18±1.61 in observation group) were also significantly difference (p=0.001 in maximum diameter and p=0.027 in aspect ratio, respectively). The most common location of aneurysms in the surgical clipping group was the MCA (49%, 79 patients), whereas that in the endovascular treatment group was the cavernous ICA (35%, 42 patients). The most common location of aneurysms in the observation group was the cavernous ICA artery (32%, 32 patients) and the MCA (19%, 19 patients). The distribution of location of UIA was significantly difference in AcoA (p=0.016), MCA (p=0.01), and cavernous ICA (p=0.001). A total of 61 patients had daughter sac, of which 56 patients were in the treated group and 5 patients were in the observation group. The ratio with daughter sac was statistically significant(p=0.001).
266 patients (95%) achieved a good outcome (Glasgow Outcome scale 5) at 1 month follow up. The mortality rate was 1%, and the overall surgical morbidity was 5%. In total 3 of the 279 patients died after the operation within 1 month. 1 death was due to intraoperative rupture and 2 due to sepsis. Twelve patients had a GOS of 4 after 1 month, these patients showed 3rd nerve palsy diplopia and short term memorial impairment. 2 patients had a GOS 3 or 2 and showed hemiparesis and severe cognitive dysfunction.
Tables 2 and 3 demonstrate the results of logistic regression analysis of associations between rupture risk factors and treatment. Univariate analyses showed that young patient age (OR=0.970, p=0.007), smoke history (OR=2.252, p=0.013), high height of aneurysms (OR=1.340, p=0.001), large width (OR=1.142, p=0.006), large maximum diameter (OR=1.192, p=0.001), large aspect ratio (OR=1.493, p=0.024), AcoA (OR=2.209, p=0.016), MCA (OR=2.064, p=0.011), and present daughter sac (OR=3.317, p=0.001) were significantly associated with the treated group. However, cavernous ICA was associated with the observation group (OR=-0.420, p=0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed that a high height of aneurysm (OR=1.906, p=0.001), a small aspect ratio (OR=0.493, p=0.006), the presence of daughter sac (OR=4.072, p=0.001), and young age (OR=0.959, p=0.001) were significantly associated with the treated group. Further associated with the treated group were AcoA and MCA (OR=3.729, p=0.022 and OR=4.110, p=0.009, respectively).
Our study found the following factors as significant between treated and observation group: age, smoke history, aneurysmal height and width, maximum diameter, aspect ratio, aneurysm located in AcoA.
MCA, Cavernous ICA and daughter sac. The significant factors for the treated group were different than those for the observation group and included the following: young mean age (58.49 years vs 61.9 years), more patients with a smoke history (25% patients vs 13% patients), high height (5.13 mm vs 3.37 mm ) and width (5.62 mm vs 4.08 mm), a large maximum diameter (6.27 mm vs 4.27 mm), large aspect ratio(1.46 vs 1.18), more AcoA location (24% vs 12%), MCA (32% vs 19%), less cavernous ICA (16% vs 34%) and more daughter sac (56% vs 5%).
In a multivariate analysis, young age, high height, small aspect ratio, presence of daughter sac, and UIA located in AcoA and MCA were independently associated with the treatment group. The effect of age as a risk factor of the rupture of UIA has been consistently reported in the past. Rinkel et al. and Vlak et al. described a higher incidence rate of SAH among older populations22,32). In our study, young age was significantly associated with the treated group. This is presumably due to the reason that treatment is recommended and implemented in younger patients because of their better general condition than those of older patients. Several researchers reported that the size and location of aneurysm were predictors of UIA rupture. The International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms [ISUIA] in 1998 demonstrated a low rupture rate for an unruptured aneurysm smaller than 7 mm. A larger size and a posterior circulation site were predictors as independent risk factors of aneurysm rupture, and patients with a history of ruptured aneurysms were at higher risk9). A Japanese cohort study reported that the following factors increased the risk of rupture: aneurysms of 7 mm or larger, aneurysms located in posterior circulation except for PcoA, and aneurysms with a daughter sac10). While recent literature recommends treatment of aneurysm that are more than 4 mm in size and multilobular or aneurysms with bleb changes4), our study showed that the most commonly treated location was the MCA and the maximum diameter was 6.27±5.26 mm. Further, the location of the aneurysm in the AcoA and MCA is significantly associated with the treated group in the multivariate analysis. MCA was easier to access in surgical clipping, and there were more cases of surgery3,5,7,18,20,23,24,27,30). While the univariate study showed that high aneurysmal height, large aneurysmal width, large maximum diameter and large aspect ratio were significantly related to the treated group, the multivariate study showed that maximum diameter and aneurysmal width did not show any difference and high aneurysmal height, small aspect ratio and daughter sac were significantly associated with the treatment group2,12,14,21). Contrary to previous studies, our study implies that a low aspect ratio was related to the treatment group25,29).
Some known risk factors did not show a significantly difference. While a female gender has been reported as risk factor in some studies10,28), more incidences of ruptured aneurysm are found in women than in men32), and, in our study the female gender was the dominant gender of total patients. However the gender was not associated with the treated group. Hypertension was a controversial risk factor as hypertension did not significantly increase the risk of rupture10). However, in other study hypertension is a major risk factor for subarachnoid hemorrhage19,32). In our study, hypertension did not show a significant difference between the treated and the observation group. Several researchers reported smoking history, alcohol history and previous episode of SAH as risk factors for UIA rupture8,10,11,15,31). In our analysis, the smoke history was significantly related to the treated group in the univariate study but not in the multivariate study, and alcohol use was not statistically significant in both analyses. In our study, we excluded patients who underwent previous episodes of SAH and symptomatic aneurysm. Further investigations of a larger number of patients is warranted to determine any significant relationships.
The indication for UIA in our institution is for patients with a tolerable whole body condition, with an aneurysm height of 5 mm or more, and with the UIA located in AcoA or MCA with or without a daughter sac. Furthermore, treatment of UIA located in MCA was usually performed by surgical clipping. Conversely, Cavernous ICA or posterior circulation aneurysms are performed mainly by endovascular treatment.
Our study has some limitations. Patient data were collected and analyzed at a single center, as a consequence, the potential for bias in treatment choice and conservative management may exist. The number of patients who were enrolled in our study was relatively small. Especially for the group of PcoA and posterior circulation, which are known to have a high risk of rupture, there was no difference between the treatment group and the observation group. It is estimated that the bias was generated fromthe limit that the subject was relatively small. We did not consider statistical errors or differences in the tendency of the operator.
Management of UIA has never been straight forward. Decisions on treatment of UIA should be carefully made after investigation of many risk factors for rupturing. In the present study, we conclude that a young age, a small aspect ratio, a large aneurysmal height, a daughter sac, and some locations of aneurysm (AcoA, MCA) are associated with the treatment group. Prospective studies should be performed in larger sample sizes and more concise evaluation to make better decisions for the treatment of UIA.
Table 1.
Comparison of the patients and aneurysmal characteristics between treated group and observation group
| Treated group (279 patients) | Observation group (100 patients) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Mean - yr | 58.49 ± 10.71 | 61.9 ± 11.11 | 0.007 |
| >70 yr – no (%) | 47 (16%) | 30 (30%) | 0.002 |
| No.of females (%) | 195 (69%) | 73 (73%) | 0.610 |
| Hypertension (%) | 164 (58%) | 52 (52%) | 0.242 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 29 (10%) | 12 (12%) | 0.708 |
| Ischemic stroke (%) | 9 (2%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Cardiac disease (%) | 17 (5%) | 5 (5%) | |
| Smoke history (%) | 70 (25%) | 13 (13%) | 0.011 |
| Alcohol (%) | 70 (25%) | 24 (24%) | 0.893 |
| Others | 53 (18%) | 18 (18%) | |
| Size of aneurysms Mean ± SD (mm) | |||
| Neck | 3.60±1.51 | 3.34±1.78 | 0.153 |
| Height | 5.13±3.39 | 3.37±3.30 | 0.001 |
| Width | 5.62±5.09 | 4.08±3.77 | 0.006 |
| Maximum diameter | 6.27±5.26 | 4.27±4.04 | 0.001 |
| Aspect ratio (%) | 1.46±0.79 | 1.18±1.61 | 0.027 |
| Location of aneurysms (%) | |||
| Anterior communicating artery | 68 (24%) | 12 (12%) | 0.016 |
| Posterior communicating artery | 31 (11%) | 11 (11%) | 0.570 |
| Middle cerebral artery | 91 (32%) | 19 (19%) | 0.010 |
| Cavernous ICA* | 46 (16%) | 34 (34%) | 0.001 |
| Internal carotid artery | 26 (9%) | 13 (13%) | 0.338 |
| Basi lar toptop | 7 (2%) | 6 (6%) | 0.114 |
| Vertebrobasilar artery | 10 (3%) | 5 (5%) | 0.554 |
| Daughter sac | 56 (20%) | 5 (5%) | 0.001 |
Table 2.
Univariate analysis between treated group and observation group
| Clinical characteristics | OR |
Univariate analysis |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 95% CI for OR (Lower-upper) | |||
| Age | 0.970 | 0.949-0.992 | 0.007 |
| No.of females | 0.859 | 0.515-1.430 | 0.558 |
| Hypertension (Positive) | 0.760 | 0.480-1.202 | 0.241 |
| Diabetes mellitus (Positive) | 1.176 | 0.575-2.404 | 0.658 |
| Smoke history (Positive) | 2.252 | 1.184-4.283 | 0.013 |
| Alcohol user (Positive) | 0.921 | 0.541-1.568 | 0.761 |
| Size of aneurysms Mean ± SD – mm | |||
| Neck | 1.126 | 0.956-1.325 | 0.155 |
| Height | 1.340 | 1.170-1.535 | 0.001 |
| Width | 1.142 | 1.038-1.256 | 0.006 |
| Maximum diameter | 1.192 | 1.077-1.319 | 0.001 |
| Aspect ratio (%) | 1.493 | 1.053-2.115 | 0.024 |
| Location of aneurysms (Positive) | |||
| Anterior communicating artery | 2.209 | 1.161-4.204 | 0.016 |
| Posterior communicating artery | 1.011 | 0.488-2.097 | 0.976 |
| Middle cerebral artery bifurcation | 2.064 | 1.180-3.608 | 0.011 |
| Cavernous ICA* | 0.420 | 0.248-0.710 | 0.001 |
| Internal carotid artery | 0.688 | 0.388-1.397 | 0.301 |
| Basilar top | 0.403 | 0.132-1.230 | 0.110 |
| Vertebrobasilar artery | 0.706 | 0.235-2.119 | 0.535 |
| Daughter sac (Positive) | 3.317 | 2.028-5.427 | 0.001 |
Table 3.
Multivariate analysis between treated group and observation group
REFERENCES
1. Bederson JB, Awad IA, Wiebers DO, Piepgras D, Haley EC Jr, Brott T, et al. Recommendations for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A Statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Stroke 2000;31:2742–2750.


2. Byoun HS, Huh W, Oh CW, Bang JS, Hwang G, Kwon OK. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms : a retrospective single center analysis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2016;59:11–16.




3. Chyatte D, Porterfield R. Nuances of middle cerebral artery aneurysm microsurgery. Neurosurgery 2001;48:339–346.


4. Seo DH, Kim DW, Park SQ, Song Y, You SH, Kwon SU, et al. Guidelines for the management of unruptured intracranial aneurysm. Korean J Cerebrovasc Surg 2011;13:279–290.
5. Dashti R, Hernesniemi J, Niemela M, Rinne J, Lehecka M, Shen H, et al. Microneurosurgical management of distal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Surg Neurol 2007;67:553–563.


6. Dusak A, Kamasak K, Goya C, Adin ME, Elbey MA, Bilici A. Arterial distensibility in patients with ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms: is it a predisposing factor for rupture risk? Med Sci Monit 2013;19:703–709.



7. Guresir E, Schuss P, Berkefeld J, Vatter H, Seifert V. Treatment results for complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms. A prospective single-center series. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2011;153:1247–1252.



8. Guresir E, Vatter H, Schuss P, Platz J, Konczalla J, de Rochement Rdu M, et al. Natural history of small unruptured anterior circulation aneurysms: a prospective cohort study. Stroke 2013;44:3027–3031.


9. The International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms--risk of rupture and risks of surgical intervention. N Engl J Med 1998;339:1725–1733.


10. Investigators UJ, Morita A, Kirino T, Hashi K, Aoki N, Fukuhara S, et al. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N Engl J Med 2012;366:2474–2482.


11. Ishibashi T, Murayama Y, Urashima M, Saguchi T, Ebara M, Arakawa H, et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: incidence of rupture and risk factors. Stroke 2009;40:313–316.


12. Jang EW, Jung JY, Hong CK, Joo JY. Benefits of surgical treatment for unruptured intracranial aneurysms in elderly patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2011;49:20–25.




14. Joo SW, Lee SI, Noh SJ, Jeong YG, Kim MS, Jeong YT. What is the significance of a large number of ruptured aneurysms smaller than 7 mm in diameter? J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2009;45:85–89.




15. Juvela S, Poussa K, Lehto H, Porras M. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke 2013;44:2414–2421.


16. Kovac JD, Stankovic A, Stankovic D, Kovac B, Saranovic D. Intracranial arterial variations: a comprehensive evaluation using CT angiography. Med Sci Monit 2014;20:420–427.



17. Li Z, Zhang G, Huang G, Wang Z, Tan H, Liu J, et al. Intraoperative combined use of somatosensory evoked potential, microvascular doppler sonography, and indocyanine green angiography in clipping of intracranial aneurysm. Med Sci Monit 2016;22:373–379.



18. Morgan MK, Mahattanakul W, Davidson A, Reid J. Outcome for middle cerebral artery aneurysm surgery. Neurosurgery 2010;67:755–761; discussion 761.



19. Murayama Y, Takao H, Ishibashi T, Saguchi T, Ebara M, Yuki I, et al. Risk analysis of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: prospective 10-year cohort study. Stroke 2016;47:365–371.


20. Ogilvy CS, Crowell RM, Heros RC. Surgical management of middle cerebral artery aneurysms: experience with transsylvian and superior temporal gyrus approaches. Surg Neurol 1995;43:15–22; discussion 22-14.


21. Park SH, Yim MB, Lee CY, Kim E, Son EI. Intracranial fusiform aneurysms: it's pathogenesis, clinical characteristics and managements. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2008;44:116–123.




22. Rinkel GJ, Djibuti M, Algra A, van Gijn J. Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review. Stroke 1998;29:251–256.


23. Rinne J, Hernesniemi J, Niskanen M, Vapalahti M. Analysis of 561 patients with 690 middle cerebral artery aneurysms: anatomic and clinical features as correlated to management outcome. Neurosurgery 1996;38:2–11.


24. Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Sughrue ME, Akhavan S, Habdank-Kolaczkowski J, Lawton MT. Current management of middle cerebral artery aneurysms: surgical results with a "clip first" policy. Neurosurgery 2013;72:415–427.



25. Ryu CW, Kwon OK, Koh JS, Kim EJ. Analysis of aneurysm rupture in relation to the geometric indices: aspect ratio, volume, and volume-to-neck ratio. Neuroradiology 2011;53:883–889.



26. Slusarz R, Beuth W, Sniegocki M. Functional capacity scale as a new tool for early functional assessment in patients after surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study involving 128 patients. Med Sci Monit 2012;18:CR680–686.



27. Suzuki J, Yoshimoto T, Kayama T. Surgical treatment of middle cerebral artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg 1984;61:17–23.


28. Thompson BG, Brown RD Jr, Amin-Hanjani S, Broderick JP, Cockroft KM, Connolly ES Jr, et al. Guidelines for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2015;46:2368–2400.


29. Ujiie H, Tachibana H, Hiramatsu O, Hazel AL, Matsumoto T, Ogasawara Y, et al. Effects of size and shape (aspect ratio) on the hemodynamics of saccular aneurysms: a possible index for surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1999;45:119–129; discussion 129-130.


30. van Dijk JM, Groen RJ, Ter Laan M, Jeltema JR, Mooij JJ, Metzemaekers JD. Surgical clipping as the preferred treatment for aneurysms of the middle cerebral artery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2011;153:2111–2117.



31. Vlak MH, Rinkel GJ, Greebe P, Algra A. Risk of rupture of an intracranial aneurysm based on patient characteristics: a case-control study. Stroke 2013;44:1256–1259.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 5,914 View
- 91 Download
- Related articles in JNIC
-
Analysis of Nitrogen Balance Test in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury2023 April;6(1)
Analysis of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Hemorrhagic Moyamoya Disease2023 April;6(1)