 |
 |
- Search
| J Neurointensive Care > Volume 7(1); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
The objective of this study is to summarize the evidence in Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews, the effects, and the benefits of monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in patients with head trauma with an indication of ICP monitoring.
Methods
The process of preparing this overview followed the guidelines established by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) for umbrella reviews. Two independent reviewers evaluated the quality of reporting, bias risk, methodologies, and evidence using three different tools: the Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews (ROBIS) instrument, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), and A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR 2).
Results
A total of five papers met the criteria for inclusion in the study. These papers consisted of 49 primary research studies and 19 unique primary research studies. One of the SRs indicated that using intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring led to a reduction in mortality. Two of the SRs had mixed results with temporal variation, while two found no significant difference in mortality with ICP monitoring. It is important to note that the quality of the SRs varied, with some being of higher quality than others.
Conclusion
There was no conclusive evidence that ICP monitoring reduces mortality in traumatic brain injury patients. There was high heterogeneity in included primary research studies. Future research should aim to address the limitations of these studies and provide more conclusive evidence regarding the effectiveness of ICP monitoring in reducing mortality in patients with traumatic brain injury.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a significant contributor to mortality and morbidity at a global level, disproportionately affecting individuals in their prime working years. This multifaceted health condition has far-reaching economic and social consequences, rendering it a significant public health concern, particularly in developing nations1). The gravity of the situation demands swift, concerted efforts to mitigate its impact and improve outcomes for those affected.
The most reliable method for monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in cases of traumatic brain injury involves the surgical placement of an intracranial sensor, which allows for direct measurement of pressure within the skull2). Three primary locations are utilized for sensor placement: intraventricular, intraparenchymal, and subdural. While this approach is highly effective for tracking patients with severe head trauma, it is also associated with a number of complications, including hemorrhage, obstruction, mispositioning, infection, and reduced accuracy in cases of asymmetric hemispheric lesions2). Furthermore, the invasive nature of this technique requires a neurosurgical procedure, which carries its own set of risks and considerations. Therefore, while intracranial sensor insertion may be the gold standard for ICP monitoring in TBI, it is important to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of this approach before proceeding with treatment.
The concept of intracranial pressure monitoring gained its popularity after the publication of brain trauma foundation (BTF) guidelines on the multimodal management of the traumatic brain injury. The multimodal monitoring suggest for the escalation of therapy in a tiered manner3). The approach for enhancing treatment for herniation syndromes is carried out in a tiered manner and ought to be executed without postponing invasive intracranial monitoring, also known as multimodal monitoring. The initial options that may be considered are placing the patient in an upright position, avoiding neck manipulation, addressing agitation and fever, attempting hyperosmolar therapy, and finally deciding whether urgent surgery is necessary. If there is clinical improvement, such as in pupil dilation or examination, these maneuvers may indicate that the patient is approaching the end of the intracranial volume-pressure curve. These crucial measures must be taken to ensure that the patient's health is preserved and that their herniation syndrome is managed effectively.
Since the start of ICP monitoring in TBI patients, there have been several studies that produce conflicting and mixed results on the outcome in TBI patients with ICP monitoring primarily mortality and length of hospital stay. Using ICP montoring to guide the patient management has its own limitations. ICP monitoring is resource intensive and time consuming and depends on the both the modality used for measurement and location of the probe. Therefore the monitoring may mislead when there is focal point of herniation. This is one of the reason why BTF guidelines recommends on ICP monitoring diffuse pathologies. It is noteworthy that in a study involving malignant stroke, a considerable number of patients exhibited a midline shift and pupillary changes despite ICP monitoring revealing an ICP < 22 mm Hg, thereby indicating that ICP values may not always reflect a concerning clinical picture4). One of the study found that the ICP montoring is as good as the clinical examination on the outcomes following TBI5).
In severe traumatic brain injury (sTBI), Intracranial pressure monitoring is the preferred method of monitoring. However, the criteria for its insertion remains unclear. The brain trauma foundation Guidelines Edition 3 provided recommendations for ICP monitoring, and in the absence of new evidence, the latest revision defaulted to those recommendations6,7). Despite this, practice surveys have shown significant variation in the use of monitoring on both individual and institutional levels, with poor adherence to BTF recommendations8,9). This implies that the decision-making process is inconsistent and poorly understood, a critical issue when assessing the efficacy of ICP monitor-based care in non-controlled studies. Furthermore, some providers may view ICP monitoring data as having little additional clinical value in uncertain situations. Therefore, there is a pressing need for a more comprehensive understanding of the criteria for ICP monitoring insertion and improved adherence to guidelines to enhance the efficacy of ICP monitoring in the management of sTBI.
The precise indications for ICP monitoring in TBI patients are unknonwn and guidelines making recommndations have low penetrance and evidence for the same. Alali et al. pubished the predictors and clinical decision making rule for selecting the ICP monitoring in TBI patients based on the clinical and radiological parameters10). However there is significant variability on the medthod of ICP monitoring and frequency. As the ICP monitoring is resource intensive, its use if often limited to high resource settings and lower resource settings use alternative methods of ICP management. Therefore there is no confirming evidence that ICP monitoring reduces mortality in TBI patients.
This overview aims to summarize the evidence in Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews, the effects, and the benefits of monitoring intracranial pressure in patients with head trauma with an indication of ICP monitoring.
We conducted an Umbrella Review to summarize the possible benefits and usefulness of monitoring intracranial pressure in patients with head trauma. This overview of reviews follows the guidelines and methodology laid down in the Joanna Briggs Institute manual for evidence synthesis in its Umbrella Review chapter11).
All patients with severe closed head trauma with an indication of intracranial pressure monitoring according to the Colombian Guidelines and the Brain trauma foundation guidelines
This review considered systematic reviews of prospective, retrospective, or cross-sectional experimental and observational studies. Systematic reviews that include reports or case series were excluded. No ongoing systematic review was considered. Systematic reviews evaluating non-invasive measurements of intracranial pressure as diameter of the optic nerve sheath were excluded.
Five electronic databases were searched systematically and iteratively by two authors independently per the defined search strategy mentioned in Supplementary Material. The following databases were searched for Systematic reviews: Cochrane Injuries Group Specialized Register (up to February 2021); The Cochrane Library (until February 2021); MEDLINE (Ovid) February 2021; EMBASE (Ovid); PubMed [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez] (February 2021); LILACS (February 2021). The search was constructed using terms and descriptors from the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) and descriptors in health sciences (DeCs) for the ILACS search and was combined with Boolean operators. The keywords for systematic reviews and meta-analysis were incorporated into the search strategy enabling it to be more sensitive and specific. In addition, the reference list of the potentially eligible studies was searched to identify more citations. The search was not limited by date or by language.
After the search, the citations found in each database were entered into the Mendeley reference manager version 1.19.4 (George Manson University, Fairfax, Virginia, USA). Two reviewers independently examined the titles and abstracts to assess eligibility. Full texts were extracted, inclusion criteria were applied, and consensus resolved disagreements. The results of the search process are shown in a PRISMA flow chart (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis) in Fig. 112). Systematic review and meta-analysis were included in the present overview if: 1) All the original studies included in the SR-MA assessed the role of ICP monitoring in head injury patients and conformed to the PICO eligibility criteria laid out a priori; 2) If at least one of the outcomes were measured in the studies included in the SR-MA.
The methodological quality of the systematic reviews of included randomized clinical trials was analyzed with the AMSTAR tool. AMSTAR is a valid, reliable, and easy-to-use tool13). It consists of 11 items and has content validity to measure methodological quality, in addition to the reliability of systematic reviews; Each of the 11 items is assigned a score of 1 if it meets the specific criteria or a score of 0 if it does not meet the criteria, is not clear, or is not applicable. The interpretation of critical appraisal is divided into three levels: 8 to 11 points are of high quality, 4 to 7 points are of moderate quality, and 0 to 3 points are of low quality. Study quality was assessed using this standardized tool by one of the reviewers and then checked by the second author. Any reviewer discrepancy was settled by mutual discussion or discussion with a third reviewer.
The risk of bias in the included studies is made through the Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews tool14). This tool is completed in three phases: (1) assess relevance (optional), (2) identify concerns with the review process, and (3) judge the risk of bias in the review. Signalling questions are included to help assess specific concerns about potential biases with the review. We omit phase 1 because not relevant to result in the risk of bias assessment.
The database search yielded 100 studies, of which fifty were removed as duplicates in the citation manager software. Fifty articles were screened for eligibility as per the title and the abstract. The full text of ten articles was retrieved for final inclusion, and five SR-MA were found eligible for inclusion in the present overview per the eligibility criteria. From the pool of reviews, a grand total of 49 distinctive and individual original articles were identified as meeting our inclusion criteria. Further analysis revealed that out of these articles, a substantial number of 43 were deemed to be appropriate for inclusion in the comprehensive meta-analyses. Among these all the SR-MA’s reported on mortality outcome in ICP monitoring group Vs non monitoring group. A total of 49 studies reported on the mortality outcome and 11 studies reported on the functional outcome and length of hospital stay. Total number of patients studies in the present overview from pool of systematic reviews were 73,085 and 61,714 patients were included in the meta-analysis.
The characteristics of the included SR-Mas are presented in Table 1. One study was published in 2012, 2014, and 2015, while two were published in 2016. Among the five SR-MA included in the present overview, one presented data from observational studies only15), one from RCTs only5) and three from a combination of observational and RCT studies16-18). From all the SR-MAs seven were RCT and rest (n=42) were observational studies. The median number of original studies included were nine with range of 2-18. Most SR-Mas included patients of both gender and all the SR-MAs included adult patients.
There was no tool for the assessment of quality mentioned in one of the SR-MA15). Cochrane risk of bias tool for the assessment of RCT and Newcastle Ottawa scale to assess the uality of observational studies was used in three SR-MAs5,16,17). One SR-MA used STROBE and Centre for Evidence Based Medicine (CBEM) criteria checklist to assess the uality of the included studies. All systematic reviews with meta-analysis (SR-MAs) included in the study demonstrated appropriate formulation of research inquiries, establishment of pre-defined and specified eligibility criteria, implementation of a systematic search methodology, and detailed reporting of primary study features and outcomes. The majority of SR-MAs conducted dual screening, evaluated for publication bias and heterogeneity. These findings suggest that while most SR-MAs adhere to standard procedures, there is still room for improvement in certain aspects of the review process, such as dual quality assessment. The authors of systematic reviews and meta-analyses employed a variety of instruments to evaluate the quality of the primary research studies. Because of the wide variety of tools used for quality assessment the quality of included studies could not be pooled together. These studies ranged from weakest evidence to strongest evidence but on a majority the included studies were of good quality. The uality assessment of included SR-MAs using AMSTAR tool showed that one of the SR-MA was of moderate uality while four included SR-MA were of high quality (Table 2). Risk of Bias Assessment with Bristol’s University ROBIS tool showed that study by Mendelson et al. was at moderate risk of bias in most of the domains of the tool, unclear in study by quesda et al. and of low risk of bias in the rest of the SR-MAs. The risk of bias by the Bristol university ROBIS tool assessment in shown in Figs. 2 and 3.
The five included SR-MAs presented comparison of 19,402 patients with ICP monitoring from a control of 53,825 patients without ICP monitoring. The types of ICP monitoring analysed in the included reviews were intraparenchymal (n=935, 4.8%), external ventricular drainage (n=620, 3.2%), epdural (n=16), combined (n=42), and not reported (n=17804, 91.7%). The summary of the included SR-MAs are shown in Table 3.
The SR-MA included studies with adult patients15). The included studies were six observational retrospective and non randomized studies with 11,371 patients. Metaanalysis was not done due to marked heterogeneity in the included studies. The main concerns in the review were non homogenous inclusion and exlcusion criteria. Individual studies did multivariate analysis but the number of variables in each varied. Quality assessment was not done but undicated the intrastudies differences due to several confunders like some of the included studies did the analysis without adjusting for the parameters of age, GCS etc.
This SR-MA included presented both systematic review and meta-analysis of the included studies from the studies including adult > 12 years including 385 patients5). Only two RCT’s were included.Cochrane risk of bias and grade tool was to assess the quality of included studies and garde strength of evidence. Monitoring had no difference from clinical examination in prognosis but the length of stay and use of hypertonic saline was less in the monitoring group. Out of the two RCTs included one had unknown risk of bias in the random sequence generation . allocation concealment, reporting bias and other biases.
The SR-MA included 18 studies, 2 RCT rest observational, including 7,637 patients with ICP monitoring and 17,862 with no ICP monitoring16). Cochrane risk of bias tool and newcastle ottawa scale was included for the quality assessment. Included RCTs had unclear risk of selection bias, detection bias, reporting bias and other biases. The results obtained were mixed results. The outcomes of the study demonstrated no significant decline in mortality rates among the ICP monitored group for those who were hospitalized before 2007, hospital mortality for the same group, and mortality in randomized controlled trials. Despite this, the overall mortality rate, mortality rate for those hospitalized after 2007, hospital mortality rate for those hospitalized after 2007, and mortality rate in observational studies for those hospitalized after 2007, along with the 2-week mortality rate and 6-month mortality rate, were reduced in the ICP monitored group. It was discovered that patients with an elevated ICP were more likely to necessitate ICP monitoring. The findings indicate that the implementation of ICP monitoring can be beneficial for certain patient groups.
The SR-MA included two RCT and seven cohort with a total of 11,038 patients17). There was no significant effect on the mortality, adverse events but the hospital stay was longer in the patients with ICP monitoring. There was considerable heterogeneity in the included studies. Cochrane risk of bias tool and Newcastle-ottawa scale was used to assess the uality assessment of the included studies.
A comprehensive analysis of 14 studies18) comprising of 24,792 patients was conducted, and it was found that there was no significant evidence to suggest that ICP monitoring was associated with a reduction in the risk of death (pooled OR 0.93 [95% CI, 0.77–1.11], p=0.40). However, the results of the meta-analysis revealed that 7 out of the 14 studies, which included 12,944 patients, and were published between January 2012 and October 2013, indicated that ICP monitoring was significantly linked with a greater reduction in mortality compared to no ICP monitoring (pooled OR 0.56 [95% CI, 0.41–0.78], p=0.0006). These findings highlight the importance of keeping up-to-date with the latest research, as newer studies may provide more accurate and reliable results. Interestingly, the 7 studies conducted in North America showed no significant evidence to suggest that ICP monitoring lowered the risk of death, which was similar to the studies conducted in other regions. Furthermore, it was found that the group subjected to ICP monitoring had significantly longer ICU LOSs (mean difference [MD] 0.29 [95% CI, 0.21–0.37]; p<0.00001). These results suggest that ICP monitoring may not always be beneficial, and further research is needed to explore its effectiveness and potential drawbacks. In conclusion, the results of the meta-analysis provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of ICP monitoring and highlight the need for continued research in this area. The pooled analysis showed that the length of hospital stay was longer in the ICP monitoring group.
There was no concusive evidence arising from the pooling of SR-MA that the ICP has efficacy in reducing the mortality. The study by Mendelson et al.15) found that the positive effect of ICP monitoring on reducing mortality, while rest of the SR-MA found no significant difference in the mortality among the two groups. Interestingly in the study by Yuan et al.18) and Shen et al.16) the wuthors found that there is temporal discrepancy in the mortality outcome with the ICP monitoring. They found that there was no significant difference among the groups on pooling the results from studies done prior to 2007 and 2012 respectively, while the later studies suugested that the ICP monitoring had beneficial effect on the mortality outcome.
This comprehensive review provides a summary of the published evidence on the impact of ICP monitoring on the duration of hospital stays, mortality rates, and procedure-related adverse events in adult patients suffering from traumatic brain injury. This review is based on a total of 49 primary research studies and 19 unique primary studies, as analyzed by the five SR-MAs. Mortality was reported as outcome in majority of the primary studies. Only one SR-MA found that the use of ICP monitoring lowered the mortality in the TBI patients15). SR-MAs found that there was no significant effect on the reduction of mortality with ICP monitoring5,17). In two SR-MAs the results varied according to the time of publication of primary studies with later studies having a positive effect of ICP monitoring on reducing the mortality while earlier studies did not find any significant effect16,18). One of the SR-MA found that the resources used in the ICU were less with the use of ICP monitoring group due to better targeted therapy5). The effect of ICP monitoring on the length of hospital stay was reduced in the ICP monitoring group in one of the SR-MA5,18) while it was prolonged in the other15). There was high heterogeneity in the SR-MAs5,15-18). The high heterogeneity in the included primary research studies could be due to the combination of different study types in the systematic reviews, heterogenous population and mode of ICP monitoring. The variables studied in each of the primary research studies were varying and that could add to the heterogeneity. Though most of the primary research studies focused on adult patients with both genders and severe traumatic brain injury, the classification of severity of the brain in jury was not uniform in all of the studies. The study by Quesda et al. was the only SR-MA that assessed the neurpsychological function as the outcome and found that there was no significant impact of ICP monitoring on the neuropsychological function of TBI patients5). The study included two RCTs and was rated as high quality of evidence; however among the two studies the study by Chestnut et al. was at low risk of bias while there was unclear risk of bias in the study by Kostic et al. domains of random sequence generation, allocation concealment, reporting bias and other biases of the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Three SR-Mas have combined the observational studies with RCTs and performed the subgroup analysis and found that though there was no significant decrease in mortality with the ICP monitoring in the RCTs, observational studies tend to show more effect of reduced mortality. These results were extracted from a pool of five SR-Mas of which one was rated of moderate quality and rest four as high quality by the AMSTAR tool. Because of high heterogeneity in the included studies included in the present overview and inclusion of RCTs and observational studies, we have high degree of certainity in the conclusions from the present overview. The findings from the present overview align with the RCTs and most of the recent systematic reviews that there is no significant effect of ICP monitoring on reducing the mortality. The studies on the procedure related events, neurpsychological outcomes and length of hospital stay are limited in number to make any meaningful conclusions and more primary research studies are required to find the association.
Shibahashi et al. have published the results of the real world experience in a propensity score matched analysis of 31,660 patients from 765 hospitals from the Japanese inpatient nationwide database and found that there was significantly reduced mortality in ICP monitoring group (31.9% vs. 39.1 %) and a longer duration of hospital stay (35 vs. 28 days) 19). The gaps in the evidence is likely to filled by more studies on the topic gathering real world experience and avoiding the potential confounders.
One of the reasons for conflicting evidence could also be due to the fact that it is not known from the primary researcg studies as to what was the objective of the placement of the ICP monitoring devices. As found in the several studies, the focus has been on utilizing the values obtained from the ICP monitoring in guiding the management, while the ICP monitoring device itself can be used to lower the ICP when placed inside the ventricles with intermittent CSF release20-22). In one of the retrospective study with different protocols of ICP monitoring from two different trauma centres, authors reported that there was no significant difference in mortality and the complications varied according to the device used for ICP monitoring23). According to a study conducted by the National Trauma Databank, the monitoring of ICPdemonstrated an association with a notable 45% rise in mortality rates. This correlation remained significant even after accounting for head Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) and Injury Severity Score (ISS) 24). The difference in outcomes with ICP monitoring in individual studies could also be due to difference in adherence to the management guidelines and delay in insertion of the ICP monitoring. As found in the study by shafi etal. The adherence and compliance was only 45%24). The strict adherence to a protocol-driven management strategy for TBI, which involves the placement of an ICPmonitor for all severe TBI (sTBI) patients, resulted in a noteworthy reduction in mortality rates that, while not statistically significant, is nevertheless noteworthy25). Furthermore, this approach also led to a marked reduction in overall costs, as well as a significant decrease in both ICU and hospital stay durations25).
This overview of reviews synthesizes the literature on the effect of ICP monitoring in traumatic brain injury patients. One of the limitation of the present study is that we have not addressed some important research questions as no systematic reviews addressed them. One of the important research question not addressed is the relationship of ICP monitoring with the radiological extent or the severity of head injury patients. Though some of the included SR-MAs did the analysis stratified on the severity of the head injury the included studies and variables studied were quite heterogenous. Though most of the included SR-MAs were of high quality, still the strength of evidence is not very strong owing to inherent limitations of the observational studies and combining RCT with observational studies in a SR-MA also leads to conflicting evidence. The technique of ICP monitoring, and method baried extensively in the included studies and more than 90% of the included primary research studies did not report on the method of ICP monitoring and this is a significant limitation. The adverse events and mortality might also get influence by the mode of ICP monitoring. One of the limitation we have found is that the results were different based on timeline and this could be due to better techniques and equipments available for ICP monitoring evolving over time. Further with time, there has been an overall improvement in the management of traumatic brain injuries across the ICUs globally and therefore a time series evaluation of effect of ICP monitoring on outcomes following TBI would yield more uniform results. The results from the present overview are conflicting from some of the larger and more recent studies published; however the aims of the present reviews was to synthesize the evidence from the existing literature of systematic reviews, these have not been accounted for.
Notwithstanding the limitations, in the present literature synthesis we have found that the studies showed mixed results on the effect of ICP monitoring in outcomes following traumatic brain injury and there is no compelling evidence that ICP monitonring reduces the mortality. We have found high heterogeneity in the studies and future studies addressing the mentioned limitations might help us to answer the question and increase the strength of evidence on use of ICP monitoring. Due to lack of evidence on the role of ICP monitoring in reducing the mortality in TBI patients, and increased use of ICP monitoring post brain trauma foundation guidelines, it has been found that more ICP targeted therapies are used in the pateints undergoing ICP monitoring. Therefore, the present overview suggest that the outcomes of ICP monitoring has been continuously evolving with time and therefore there is no compelling evidence to recommend its universal use or to remove it from use till stronger evidence is found either in support or againt ICP monitoring. ICP monitoring should be used as stated in the brain trauma foundation guidelines in an level one traumacentre facility with the availability of targeted ICP management therapies.
Supplementary Materials
Further details on supplementary materials are presented online (available at https://doi.org/10.32587/jnic.2023.00731).
NOTES
Fig. 2.
Risk of bias graph. Review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Fig. 3.
Risk of bias assessment with Bristol’s University ROBIS tool: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included systematic review.
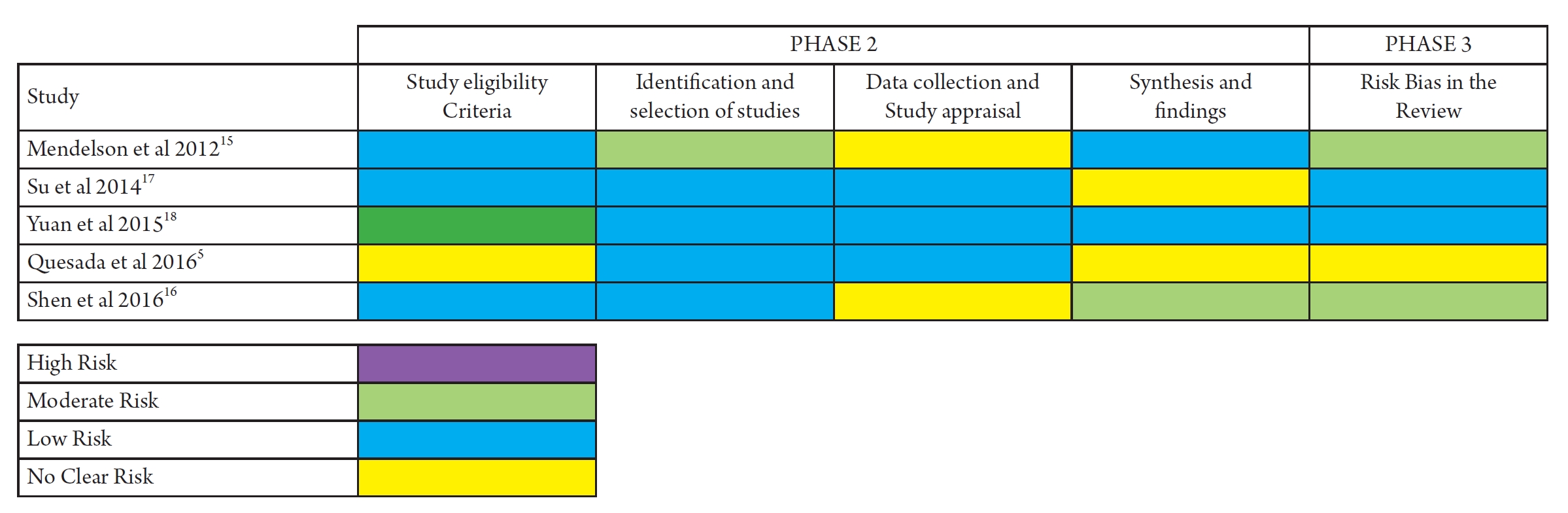
Table 1.
Characteristic of included systematic reviews and meta-analysis
| Study (Author, year) | Meta-analysis? Yes/No | Data base Search | PICO question | Outcome assessed | Risk of bias and quality assessment tool | Main Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mendelson et al 201215) | No | MEDLINE (1966-October 2011) | Use ICP monitors and mortality in TBI patients comparison not monitoring | Mortality | Not reported | The isolated benefit of ICP monitoring in severe TBI is not clearly established. Clinical evidence is lacking as to the efficacy of ICP monitoring mostly attributed to the heterogeneous nature |
| EMBASE (1977-October 2011) | of the studies available on this topic. The significant modification of signal effect by confounding variables suggests that outcomes in severe TBI relate to both the presentation of the patient and the overall delivery of care rather than specific elements within the system. | |||||
| Su et al 201417) | Yes | PUBMED | P: patients with TBI | Mortality to 6 Months | Cochrane Rias of bias assessment tool | No benefit was found in patients with TBI who underwent ICP monitoring. Considering substantial clinical heterogeneity |
| Wan fang database | I: ICP monitoring | Unfavorable outcome GOSE 1 to 4 points in Score | And | |||
| VIP data base | C: No ICP monitoring | Events adverse | New Casttle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) | |||
| O: Mortality, Unfavorable outcome, events adverse, stay ICU | Length Stay ICU | |||||
| Yuan et al 201518) | Yes | MEDLINE,EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Central) October 2013 | Monitoring ICP vs No monitoring for TBI | STROBE and Centre for Evidence Based Medicine (CBEM) criteria | The current clinical evidence does not | |
| Indicate that ICP monitoring overall is | ||||||
| Significantly superior to no ICP monitoring in terms of the mortality of TBI patients | ||||||
| Quesada et al 20165) | Yes | MEDLINE, HINARI EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) | Monitoring ICP vs No monitoring for TBI | Mortality to 6 months | Cochrane risk of bias tool and GRADE Scale | The monitoring of intracranial pressure no had an impact in terms of mortality. It also showed benefits in reducing polypharmacy and the number of interventions. |
| Good Prognosis (GOSE better than 4) | ||||||
| Poor Prognosis (GOSE 4 or less) | ||||||
| Length of Stay ICU | ||||||
| Stay ICU with specific cerebra support | ||||||
| Shen et al 201616) | Yes | EMBASE, PUBMED, and the Cochrane Library | P: patients with TBI | Mortality in sub-groups | Cochrane risk of bias tool and New Casttle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) | Superior survival was observed in severe TBI patients with ICP monitoring, yet the role of ICP monitoring in severe TBI patients remain to be further elucidated, more rigorously designed |
| I: ICP monitoring | Overall mortality | studies with long-term follow-up on the effects of ICP monitoring are needed | ||||
| C: No ICP monitoring | Mortality in ICU | |||||
| O: Mortality | Mortality in 2 to 6 weeks |
Table 2.
AMSTAR tool: assessment to methodological quality on systematic review included
| Study |
AMSTAR Questions |
Quality of systematic review | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Total | ||
| Mendelson et al 201215) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | NA | No | Yes | 6/11 | Moderate |
| Su et al 201417) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9/11 | High |
| Yuan et al 201518) | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9/11 | High |
| Quesada et al 20165) | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | 8/11 | High |
| Shen et al 201616) | Yes | NR | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9/11 | High |
Table 3.
Summary of systematic reviews included in this Umbrella review
| Study | N | Type of included Studies | Type of ICP monitor | Quality of included studies | Results of Outcome with heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mendelson et al 201215) | 11,434 | Retrospective observational studies: 8 | Intraparenchymal: 203 (8.46%) | Not Reported | Mortality |
| ICP monitoring: 2,717 | Total: 8 | EVD: 124 (4.56%) | OR 0.77, p =0.015 | ||
| Control: 8,717 | Epidural: 8 (0.29%) | 28-day Mortality | |||
| Combined: 21(0.77%) | OR 2.1 [95% CI, 0.80–5.6] p =0.13 | ||||
| Not reported: 2,361 (86.9%) | Heterogeneity: Not Applicable | ||||
| Su et al 201417) | 11,143 | RCT: 2 | Not Reported | NOS score | Mortality |
| ICP monitoring: 3,282 | Retrospective Observational Studies: 7 | High (8–9): 4 (44.44%) | OR 1.16 [95% CI, 0.87–1.54] p=0.31 I2=80% | ||
| Control: 7,861 | Total: 9 | Moderate (5–7): 3 (33.33%) | Heterogeneity: High | ||
| Low (0–4): 0 (0%) | Unfavorable Outcome: OR 1.40 [95% CI, 0.99–1.98] p=0.06 I2=4% | ||||
| Not Reported: 2 (22.22%) | Heterogeneity: Low | ||||
| Adverse events: OR 1.04 [95% CI, 0.64–1.70] p=0.87 I2=78% | |||||
| Heterogeneity: High | |||||
| Length of hospital stay | |||||
| Mean differences 6.32 [95% CI, 4.9–7.75] p<0.0001 I2=99% | |||||
| Heterogeneity: Very High | |||||
| Yuan et al 201518) | 24,792 | RCT: 1 | Intraparenchymal: 732 (10.81%) | STROBE Check list | Mortality |
| ICP monitoring: 6,744 | Retrospective Observational Studies: 9 | EVD: 339 (5.02%) | High: 16–20: 10 (71.43%) | In ICU: OR 0.92 [95% CI, 0.79–1.06] p=0.26 I2=41% | |
| Control: 18,048 | Prospective Observational Studies: 4 | Epidural: 8 (0.12%) | Moderate 11–15:2 (14.28%) | Heterogeneity: Low | |
| Total: 14 | Combined: 21(0.31%) | Low: ≤ 10:1 (0.714%) | In Hospital OR 1.06 [95% CI, 0.8–1.42] p=0.68 I2=84% | ||
| Not reported: 5644 (83.69%) | Not Reported: 1 (0.714%) | Heterogeneity: High | |||
| Length ICU stay | |||||
| CEBM strength of evidence | Mean differences 0.29 [95% CI, 0.3–0.32] p<0.0001 I2=93% | ||||
| 4: n=6 | Heterogeneity: Very High | ||||
| 2b: n=4 | Length Hospital stay | ||||
| 3b: n=3 | Mean differences 0.21 [95% CI, 0.04–0.37] p=0.01 I2=100% | ||||
| 1b: n=1 | Heterogeneity: High | ||||
| Quesada et al 20165) | 358 | RCT: 2 | EVD: 157 (89.2%) | GRADE Scale | Mortality RR 0.85 [95% CI, 0.67–1.07] p =0.17 I2=0% |
| ICP monitoring: 176 | Not Reported: 34 (19.32%) | High Quality: 2 (100%) | Heterogeneity: Low | ||
| Control: 182 | Outcomes | ||||
| Good RR 1.05 [95% CI, 0.84–1.31] p=0.69 I2=20% | |||||
| Heterogeneity: Low | |||||
| Poor RR 0.95 [95% CI, 0.79–1.15] p=0.60 I2=0% | |||||
| ICU Stay | |||||
| Overall | |||||
| Mean differences 3 [95% CI, 2–4] p<0.0001 | |||||
| Heterogeneity: Not applicable | |||||
| With Specific support for brain injuries | |||||
| Mean differences –1.4 [95% CI, –2.37 to –0.43] p<0.0001 | |||||
| Heterogeneity: Not applicable | |||||
| Shen et al 201616) | 25500 | RCT: 2 | Not reported | NOS score | Mortality: |
| ICP monitoring: 6,483 | Retrospective Observational Studies: 16 | High (8–9): 14 (77.77%) | Overall Risk Ratio 0.85 [95% CI, 0.73–0.98] p=0.02 I2=84% | ||
| Control: 19,017 | Total: 18 | Moderate (5–7): 2 (11.11%) | Heterogeneity: High | ||
| Low (0–4): 0 (0%) | In Hospital: | ||||
| Not Reported: 2 (11.11%) | Before 2007: Risk Ratio 1.18 [95% CI, 0.89–1.56] p=0.25 I2=86% | ||||
| Heterogeneity: High | |||||
| After 2007: Risk Ratio 0.72 [95% CI, 0.63–0.83] p<0.00001 I2=68% | |||||
| Heterogeneity: High | |||||
| ICU mortality: Risk Ratio 1.01 [95% CI, 0.9–1.13] p=0.85 I2=0% | |||||
| Heterogeneity: Low |
ICP: Intracranial pressure, EVD: External ventricular drainage, RCT: randomized controlled trial, NOS: New Casttle-Ottawa Scale, STROBE: STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology, ICU: Intensive care unit, CEBM: The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, GRADE: The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation.
REFERENCES
1. Carteri RB, Silva RA. Traumatic brain injury hospital incidence in Brazil: an analysis of the past 10 years. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2021;33:282–289.



2. Nag DS, Sahu S, Swain A, Kant S. Intracranial pressure monitoring: Gold standard and recent innovations. World J Clin Cases 2019;7:1535–1553.



3. Chesnut R, Aguilera S, Buki A, Bulger E, Citerio G, Cooper DJ, et al. A management algorithm for adult patients with both brain oxygen and intracranial pressure monitoring: the Seattle International Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Consensus Conference (SIBICC). Intensive Care Med 2020;46:919–929.




4. Poca MA, Benejam B, Sahuquillo J, Riveiro M, Frascheri L, Merino MA, et al. Monitoring intracranial pressure in patients with malignant middle cerebral artery infarction: is it useful? J Neurosurg 2010;112:648–57.


5. Quesada MF, Duran MA, Laiseca EF, Flórez WA. Una revisión sistemática del monitoreo de la presión intracraneana en adultos con trauma craneoencefálico severo. Revista Chilena de Neurocirugía 2019;42:160–167.


6. Brain Trauma Foundation; American Association of Neurological Surgeons; Congress of Neurological Surgeons. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 2007;24 Suppl 1:S1–106.
7. Carney N, Totten AM, O'Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery 2017;80:6–15.

8. Bulger EM, Nathens AB, Rivara FP, Moore M, MacKenzie EJ, Jurkovich GJ, Brain Trauma Foundation. Management of severe head injury: institutional variations in care and effect on outcome. Crit Care Med 2002;30:1870–1876.


9. Sivakumar S, Taccone FS, Rehman M, Hinson H, Naval N, Lazaridis C. Hemodynamic and neuro-monitoring for neurocritically ill patients: An international survey of intensivists. J Crit Care 2017;39:40–47.


10. Alali AS, Temkin N, Barber J, Pridgeon J, Chaddock K, Dikmen S, et al. A clinical decision rule to predict intracranial hypertension in severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 2018;131:612–619.



11. Aromataris E, Munn Z. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. 2020. https://jbi-global-wiki.refined.site/space/MANUAL. [Accessed Apr 8 2022].
12. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000097.



13. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017;358:j4008.



14. Whiting P, Savović J, Higgins JP, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, et al, ROBIS group. ROBIS: A new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol 2016;69:225–234.



15. Mendelson AA, Gillis C, Henderson WR, Ronco JJ, Dhingra V, Griesdale DE. Intracranial pressure monitors in traumatic brain injury: a systematic review. Can J Neurol Sci 2012;39:571–576.


16. Shen L, Wang Z, Su Z, Qiu S, Xu J, Zhou Y, et al. Effects of intracranial pressure monitoring on mortality in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 2016;11:e0168901.



17. Su SH, Wang F, Hai J, Liu NT, Yu F, Wu YF, et al. The effects of intracranial pressure monitoring in patients with traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 2014;9:e87432.



18. Yuan Q, Wu X, Sun Y, Yu J, Li Z, Du Z, et al. Impact of intracranial pressure monitoring on mortality in patients with traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 2015;122:574–587.


19. Shibahashi K, Ohbe H, Matsui H, Yasunaga H. Real-world benefit of intracranial pressure monitoring in the management of severe traumatic brain injury: a propensity score matching analysis using a nationwide inpatient database. J Neurosurg 2023;139:1514–1522.


20. Chesnut RM, Aguilera S, Buki A, Bulger EM, Citerio G, Cooper DJ, et al. Perceived utility of intracranial pressure monitoring in traumatic brain injury: a seattle international brain injury consensus conference consensus-based analysis and recommendations. Neurosurgery 2023;93:399–408.



21. Chesnut RM, Temkin N, Carney N, Dikmen S, Rondina C, Videtta W, et al, Global Neurotrauma Research Group. A trial of intracranial-pressure monitoring in traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med 2012;367:2471–2481.



22. Chesnut RM, Bleck TP, Citerio G, Classen J, Cooper DJ, Coplin WM, et al. A consensus-based interpretation of the benchmark evidence from South American Trials: treatment of intracranial pressure trial. J Neurotrauma 2015;32:1722–1724.


23. Guyot LL, Dowling C, Diaz FG, Michael DB. Cerebral monitoring devices: analysis of complications. Acta Neurochir Suppl 1998;71:47–49.