 |
 |
- Search
| J Neurointensive Care > Volume 4(1); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
In patients with malignant middle cerebral infarction (MMI), early decompressive hemicraniectomy (DHC) is well-known to reduce mortality and improve clinical outcome. Nevertheless, its effectiveness in clinical outcomes has only been confirmed by defining outcomes in terms of the modified Rankin scale (mRS), and many studies have already suggested that survival with severe dependency, such as mRS 4 or 5, is not acceptable. However, several other important domains are closely related to quality of life, such as consciousness or cognition, and these are not directly measured in the mRS. Therefore, the present study aimed to identify significant factors associated with poor consciousness, such as minimally conscious state (MCS) or vegetative state (VS) in patients undergoing DHC to treat MMI.
Methods
Between January 2011 and December 2017, 22 patients who survived from MMI after DHC and had more than 6 months of follow-up were enrolled our study. Clinical outcomes 6 months after DHC were measured, and the patients were divided into two groups based on their level of consciousness. Preserved consciousness was categorized as a favorable outcome, while poor consciousness such as MCS or VS constituted an unfavorable outcome. Clinical and radiological variables using volumetric measurement were analyzed to identify factors that were significantly associated with unfavorable outcome.
Results
Of the entire cohort, eight patients (36.36%) were placed in the unfavorable outcome (MCS or VS) 6 months after DHC to treat MMI. In univariate and multivariate logistic analysis, only infarction volume in the preoperative CT was a significant independent predictor of unfavorable outcome (odds ratio: 1.021, 95% confidence interval: 1.001–1.042, p = 0.023).
Malignant middle cerebral artery infarction (MMI) is a devastating disease that inevitably leads to either death or severe disability2,12,13,23). Early decompressive hemicraniectomy (DHC) is a well-known treatment for MMI that reduces mortality and improves clinical outcomes, according to several randomized controlled trials13,23). However, most previous studies regarding the effectiveness of DHC in MMI treatment have focused on mortality rather than long-term neurological disability5,12, 26, 27). In addition, studies evaluating the effect of this treatment on clinical outcomes have defined favorable outcomes using the modified Rankin scale (mRS), which focuses on degree of disability without considering patients’ consciousness29). More specifically, the mRS does not reflect real favorable outcomes because it fails to take into account several important domains, namely cognition, language, visual function, and emotional impairment, which are closely related to quality of life16). Therefore, the framing of acceptable outcome after DHC to treat MMI must be reconsidered.
Even when patients survive MMI, those with poor consciousness, such as vegetative state (VS) or minimally conscious state (MCS), exert an emotional and financial burden on their families2). Considering both these burdens and the current consensus, we believe that the decision to perform DHC to treat MMI should be based on the patient’s chance of achieving an individually acceptable long-term outcome, rather than simply on their chance of survival. In particular, clinicians should take into account the patient’s predicted level of consciousness.
Hence, identifying the prognostic factors associated with poor consciousness after DHC to treat MMI will allow more considered counselling with patient’s families before DHC and inform clinical decision making regarding whether to perform surgery based on the patient’s expressed will12). In this respect, the present study aimed to identify the significant factors associated with poor consciousness in patients undergoing DHC to treat MMI. To our knowledge, it was the first study to define “unfavorable outcome” as poor consciousness and elucidate which factors were significantly associated with that outcome.
All patients who underwent DHC to treat MMI at our hospital between January 2011 and December 2017 were enrolled in the present study. We reviewed all relevant medical records and surgical reports and collected both clinical and radiological data. Specifically, the clinical data comprised the patients’ age, sex, comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, atrial fibrillation), initial National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, Acute Physiology, Age, Chronic, Health Evaluation 2 (APACHE II) score, interval from MMI to DHC, dominant side, changes to pupil size or response, and success of recanalization before DHC. The radiological data consisted of midline-shift on pre-operative studies (pineal gland displacement), presence of intracerebral or intraventricular hemorrhage, basal cistern effacement, DHC bone flap size, and infarction volume on preoperative CT scan.
Based on the patients’ level of consciousness 6 months after DHC, clinical outcome was dichotomized as favorable or unfavorable. The favorable outcome included patients who had preserved conscious awareness and could communicate with their relatives, while the unfavorable outcome was composed of patients who showed poor consciousness such as MCS or VS, which were diagnosed according to previous studies9,14). Institutional review board approval was obtained for this retrospective study, and informed consent was waived due to its retrospective nature.
Preoperative cerebral CT scan was performed using multidetector scanning with a bone algorithm. The following parameters were used: display field of view, 15–18 cm; tube current, 80/100 mA; tube voltage, 120 KV. Axial images had a slice thickness of 1-mm with coronal and sagittal reconstructions. All images from the preoperative CT were stored in DICOM format; quantitative infarction volume was then calculated using the 3D tool from OsiriX MD (Pixmeo, Geneva, Switzerland). On the axial CT images, low density area was manually outlined in every slice (Fig. 1A). The images were inspected visually to identify whether all the low density outlines in every single axial slice had been extracted correctly. The 3D tool was then used to create a 3D model and measure the cerebral infarction volume. This tool allows volume to be measured based on various consecutive areas within the region of interest (Fig. 1B and C). The DHC bone flap size was calculated using the same image analysis program. The bone defect in each patient’s postoperative lateral plain X-ray was outlined manually, and the area of the region was measured.
DHC was performed when the patients with MMI showed poor neurological status combined with space-occupying cerebral swelling, as visualized on CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A standard frontotemporoparietal craniectomy was performed and stellate fashion duroplasty was conducted. The craniectomy was made as large as possible basally and in the anteroposterior direction, with aggressive decompression of the temporal lobe to prevent uncal herniation. In all patients, immediate postoperative cerebral CT scan was carried out to rule out procedural complications and confirm the status of the infarction area. After surgery, patients were transferred to the intensive care unit; their intracranial pressure (ICP) was monitored and they remained intubated and sedated until it was within the normal range. The critical ICP threshold was defined as an ICP > 20 mmHg for longer than 10 minutes. This was treated using aggressive osmotic therapy and additional deep sedation. Blood pressure, electrolytes, glucose, and blood gases were strictly controlled.
Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and as frequency or percentage for categorical variables. For continuous values, between-group difference was determined using the independent student’s t-test or the Mann–Whitney U test, depending on statistical distribution. For categoric values, between-group differences were determined using chi-square statistics or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate.
Univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses were conducted for unfavorable consciousness. All factors that showed significance in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis. A p-value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses in the present study were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (Version 21; IBM, Armonk, New York).
A total of 34 patients were included; of these, eight (23.53%) were excluded because they died in the period of acute management for increased intracranial pressure (IICP) after DHC. Two patients who showed large hemorrhagic transformation with infarction upon admission were also excluded, as were two who did not re-visit our hospital after discharge. Hence, our study involved 22 patients who survived MMI after DHC were followed up for more than 6 months (Fig. 2).
The baseline demographics and details of both the entire cohort and the two groups (favorable consciousness and unfavorable consciousness) are shown in Table 1. Across the entire cohort, a total of eight patients (36.36%) showed either MCS or VS 6 months after DHC and were included in unfavorable outcome, while 14 patients (63.64%) had preserved consciousness and were included in favorable outcome. The unfavorable outcome contained more patients who showed changes in pupil size or response before DHC (odds ratio [OR]: 39.00, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 3.600–96.000, p = 0.002). Furthermore, APACHE II score was significantly higher in the unfavorable outcome than in the favorable outcome (16.12 ± 2.10 vs. 12.07 ± 3.62, p = 0.009), and patients in the unfavorable outcome had larger infarction volume than those in the favorable outcome (527.79 ± 116.89 vs. 331.40 ± 77.71, p ≤ 0.001) (Fig. 3).
Univariate analysis showed that the following parameters were associated significantly with unfavorable outcome: changes in pupil size or response before DHC (OR: 39.00, 95% CI: 2.933–518.84, p = 0.006), higher APACHE II score (OR: 1.80, 95% CI: 1.06–3.04, p = 0.028), larger infarction volume (OR: 1.022, 95% CI: 1.004–1.039, p = 0.013), while multivariate analysis only confirmed infarction volume as a significant independent predictor of unfavorable outcome (OR: 1.021, 95% CI: 1.001–1.042, p = 0.036) (Table 2).
The current study demonstrated that the proportion of patients with poor consciousness such as MCS or VS 6 months after DHC to treat MMI was 36.36%, and that infarction volume measured in the preoperative CT scan was an independent predictor of poor consciousness. To our knowledge, it was the first attempt to define ubfavorable outcome as poor consciousness and elucidate which factors were significantly associated with this outcome.
Several tools exist to measure stroke outcomes, the most widely used of which are the NIHSS score, mRS, and the Barthel index. In particular, the mRS is commonly used to assess the level of disability after stroke and can be used to guide rehabilitation plans. However, some factors that are closely related to the quality of life, such as consciousness, cognition, language, visual functions, and emotional impairment, are not directly measured in this scale6,7,16).
In their review and meta-analysis of large middle cerebral artery infarction, Alexender et al. reported that the rate of severe dependency among patients who underwent DHC to treat MMI was 80%2). Meanwhile, Hecht et al. demonstrated that the proportion of patients with severe disability (mRS < 3) 12 months after DHC to treat MMI was 80.2%12). Therefore, given that most patients undergoing DHC to treat MMI cannot avoid hemiplegia or severe hemiparesis (mRS < 3) and are likely to remain dependent, it may be unreasonable to define “unfavorable outcome” simply as “dependency” (mRS < 3), which focuses on level of disability only. Hence, the definition of “unfavorable outcome” in survivors after DHC to treat MMI should be reconsidered.
The paradox of disability refers to how patients’ perceptions of personal health, well-being, and life satisfaction are often discordant with their objective health status and disability1).
In real practice, especially in the treatment of patients with severe disability who have survived stroke, clinicians often encounter the paradox of disability: Why do many patients with serious and persistent disabilities report that they experience good or excellent quality of life when, to most external observers, they seem to have an undesirable daily existence?”
In a stroke study carried out by Honeybul, more participants changed their attitude to define mRS ≤ 4 (dependency) as an acceptable outcome after this concept of disability paradox was introduced13). This alteration in the participants’ attitude to dependency originated from the belief that despite severe disability, patients can be happy and experience good quality of life. Nonetheless, to feel or experience happiness or satisfaction in life, well-preserved consciousness is essential, so we redefined favorable clinical outcome after DHC to treat MMI based on the patients’ level of consciousness, regardless of their level of disability.
In the group comparison and univariate analysis of unfavorable outcome, three factors had a significant relation to poor consciousness: changes in pupil size or response before DHC, higher APACHE II score, and infarction volume as measured in the preoperative CT scan.
Areflexia of pupil response or anisocoria of pupil sign reflects damage to the brain stem due to herniation, which confers an increased risk of irreversible brain injury. Many previous studies have suggested that early DHC before signs of brain stem herniations appear, such as pupillary change, can improve mortality and clinical outcomes10,17,21,22,24). In line with these previous findings, the present study also demonstrated that areflexia of pupil response is significantly related with poor consciousness. To assess the physiological conditions of each patient with MMI, APACHE II score was applied and calculated in every case. The APACHE II score is among the most widely used scales to predict outcome in patients in intensive care units (ICUs); it was originally developed to describe groups of ICU patients and evaluate medical treatment30). The score considers 12 variables of the most commonly measured physiological factors, comprising three main components: vital signs (heart rate, mean blood pressure, respiratory rate, temperature and Glasgow coma score), variables derived from routine venous blood tests (hematocrit, white blood cell count, serum potassium, serum sodium and serum creatinine), and variables derived from routine arterial blood tests (serum pH and PaO2). In our analysis of group comparisons and univariate analysis, APACHE II score was significantly correlated with poor consciousness 6 months after DHC, probably because APACHE II score can capture extremes of various physiological parameters that may cause more brain injury (i.e. blood pressure, hypoxia, fever, and other signs of systemic inflammation) 20). Within this scoring system, the Glasgow coma scale is a well-known significant predictor of clinical outcome in patients with various diseases, and it may play an important role in predicting outcome4).
With technical advances and greater availability of radiological image analysis software, more objective ways to measure the actual volume of the infarction, as well as other diseases such as intracranial hemorrhage or masses, have been introduced and applied in various clinical studies8,12,15,18,19,25). In some of these, lesion volume was a better predictor of outcome than traditional qualitative scales15,18). The present study suggested, by both univariate and multivariate analyses, that volume of infarction is more closely correlated with favorable clinical outcome, based on the level of consciousness, than other previous qualitative scales.
Contrary to our expectation, dominant hemisphere was not found to be a predictor of poor consciousness in the present study, showing no significant difference in group comparison analysis. Specifically, eight of 13 patients (61.54%) with infarction in the dominant hemisphere showed favorable outcome 6 months after DHC, and six of nine patients (66.67%) with infarction in the non-dominant hemisphere were included in the favorable outcome. Consistent with our findings, a previous study by Kilincer et al. that focused on large hemispheric infarction also showed that dominance was not correlated with clinical outcome. The authors advocated that dominant hemisphere infarction should not be an exclusion criterion when deciding whether to perform DHC to treat MMI17). In particular, we assumed that the recovery of language function can be explained in terms of neuroplasticity and of functional compensation by the non-dominant hemisphere during the 6 months following stroke. This assumption is in line with the findings of previous publications3,11,28).
The present study had several limitations. First, it was a retrospective, single-center investigation with a small sample size. Furthermore, the method used to calculate infarct volumes was not fully automated, so it inevitably had interobserver bias. Hence, to draw a more general conclusion, further prospective study with a larger sample size is needed, and fully automated techniques should be developed to allow volume calculation without interobserver bias.
Given that most patients undergoing DHC to treat MMI are likely to have severe dependency, with an mRS 4 or 5, it might be unreasonable to define unfavorable outcome based on mRS, which focuses on level of disability. The present study suggested that defining unfavorable outcome based on the level of consciousness to reflect quality of life should be considered. We identified infarction volume as a significant predictor of poor consciousness.
Fig. 1.
The process of Image analysis using the OsiriX MD program (Pixmeo, Geneva, Switzerland). (A) On the axial computed tomography images, the low density areas were manually outlined in every single slice. The images were inspected visually to identify whether all the low density outlines in every single axial slice had been extracted correctly. (B-C) The 3D tool was then used to create a 3D model and measure cerebral infarction volume.
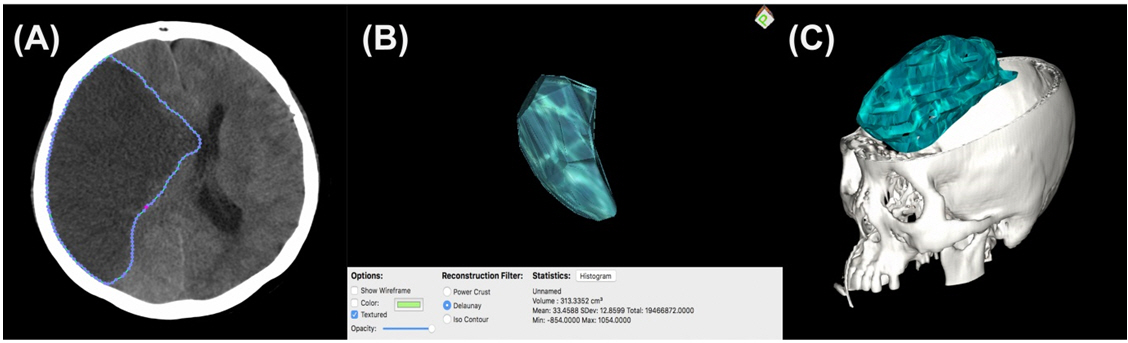
Fig. 2.
Inclusion criteria. DHC: Decompressive hemicraniectomy, MMI: Malignant middle cerebral infarction, IICP: Increased intracranial pressure, ICH: Intracerebral hemorrhage.

Fig. 3.
Box plots between the favorable and unfavorable outcome groups. APACHE II was significantly higher in the unfavorable outcome group than in the favorable outcome group (16.12±2.10 vs. 12.07±3.62, p = 0.009), and patients in the unfavorable outcome group had larger infarction volume than those in the favorable outcome group (541.38±98.76 vs. 331.40±77.71, p ≤ 0.001).
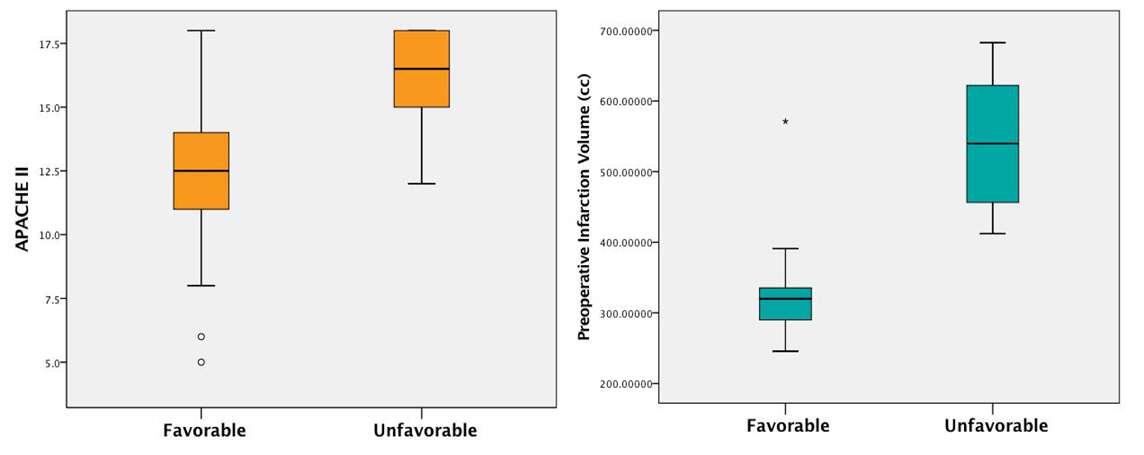
Table 1.
Baseline demographics
| Entire cohort (n = 22) | Favorable (n = 14) | Unfavorable (n = 8) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years)† | 58.09 ± 10.35 | 58.14 ± 10.65 | 58.00 ± 10.52 | 0.973 |
| Female (%)‡ | 5/22 | 4/14 | 1/8 | 0.613 |
| HTN (%) | 7/22 | 3/14 | 4/8 | 0.343 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 3/22 | 2/14 | 1/8 | > 0.99 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 8/22 | 5/14 | 4/8 | > 0.99 |
| Pupil areflexia (%) | 7/22 | 1/14 | 6/8 | 0.002* |
| Dominant side (%) | 13/22 | 8/14 | 5/8 | > 0.99 |
| Initial NIHSS | 16.22 ± 2.87 | 16.07 ± 2.73 | 16.50 ± 3.29 | 0.714 |
| APACHE Ⅱ | 13.54 ± 3.68 | 12.07 ± 3.62 | 16.12 ± 2.10 | 0.009* |
| Tissue plasminogen activator (%) | 6/22 | 44330 | 44263 | > 0.99 |
| Recanalization (%) | 6/22 | 44330 | 44204 | 0.351 |
| Interval between stroke and DHC (hours) | 52.91 ± 27.38 | 60.00 ± 26.20 | 40.50 ± 26.39 | 0.082 |
| Midline shift (mm) | 11.17 ± 3.71 | 10.28 ± 3.66 | 12.73 ± 3.46 | 0.188 |
| Basal cistern effacement (%) | 19/22 | 11/14 | 8/8 | 0.273 |
| The ICH presence (%) | 13/22 | 8/14 | 5/8 | > 0.99 |
| Infarction volume (mm3) | 408.10 ± 133.03 | 331.40 ± 77.71 | 541.38 ± 98.76 | < 0.001* |
| DHC size (cm2) | 124.96 ± 19.61 | 120.95 ± 17.54 | 131.95 ± 22.23 | 0.275 |
Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate binary logistic analysis for unfavorable outcome
REFERENCES
1. Albrecht GL, Devlieger PJ. The disability paradox: high quality of life against all odds. Soc Sci Med 1999;48:977–988.


2. Alexander P, Heels-Ansdell D, Siemieniuk R, Bhatnagar N, Chang Y, Fei Y, et al. Hemicraniectomy versus medical treatment with large MCA infarct: a review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016;6:e014390.



3. Blasi V, Young AC, Tansy AP, Petersen SE, Snyder AZ, Corbetta M. Word retrieval learning modulates right frontal cortex in patients with left frontal damage. Neuron 2002;36:159–170.


4. Claassen J, Vu A, Kreiter KT, Kowalski RG, Du EY, Ostapkovich N, et al. Effect of acute physiologic derangements on outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care Med 2004;32:832–838.


5. Daou B, Kent AP, Montano M, Chalouhi N, Starke RM, Tjoumakaris S, et al. Decompressive hemicraniectomy: predictors of functional outcome in patients with ischemic stroke. J Neurosurg 2016;124:1773–1779.


6. Dromerick AW, Edwards DF, Diringer MN. Sensitivity to changes in disability after stroke: a comparison of four scales useful in clinical trials. J Rehabil Res Dev 2003;40:1–8.

7. Duncan PW, Wallace D, Lai SM, Johnson D, Embretson S, Laster LJ. The stroke impact scale version 2.0. Evaluation of reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change. Stroke 1999;30:2131–2140.


8. Garcia S, Torne R, Hoyos JA, Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Amaro S, Llull L, et al. Quantitative versus qualitative blood amount assessment as a predictor for shunt-dependent hydrocephalus following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 2018;136:1743–1750.
9. Giacino JT, Ashwal S, Childs N, Cranford R, Jennett B, Katz DI, et al. The minimally conscious state: definition and diagnostic criteria. Neurology 2002;58:349–353.


10. Hacke W, Schwab S, Horn M, Spranger M, De Georgia M, von Kummer R. 'Malignant' middle cerebral artery territory infarction: clinical course and prognostic signs. Arch Neurol 1996;53:309–315.


11. Hamilton RH, Chrysikou EG, Coslett B. Mechanisms of aphasia recovery after stroke and the role of noninvasive brain stimulation. Brain Lang 2011;118:40–50.



12. Hecht N, Neugebauer H, Fiss I, Pinczolits A, Vajkoczy P, Juttler E, et al. Infarct volume predicts outcome after decompressive hemicraniectomy for malignant hemispheric stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2018;38:1096–1103.


13. Honeybul S, Ho KM, Blacker DW. ORACLE Stroke Study: Opinion Regarding Acceptable Outcome Following Decompressive Hemicraniectomy for Ischemic Stroke. Neurosurgery 2016;79:231–236.

15. Jimenez-Roldan L, Alen JF, Gomez PA, Lobato RD, Ramos A, Munarriz PM, et al. Volumetric analysis of subarachnoid hemorrhage: assessment of the reliability of two computerized methods and their comparison with other radiographic scales. J Neurosurg 2013;118:84–93.


17. Kilincer C, Asil T, Utku U, Hamamcioglu MK, Turgut N, Hicdonmez T, et al. Factors affecting the outcome of decompressive craniectomy for large hemispheric infarctions: a prospective cohort study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2005;147:587–594; discussion 594.


18. Ko SB, Choi HA, Carpenter AM, Helbok R, Schmidt JM, Badjatia N, et al. Quantitative analysis of hemorrhage volume for predicting delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2011;42:669–674.


19. Lagares A, Jimenez-Roldan L, Gomez PA, Munarriz PM, Castano-Leon AM, Cepeda S, et al. Prognostic Value of the Amount of Bleeding After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: a Quantitative Volumetric Study. Neurosurgery 2015;77:898–907; discussion 907.


20. Lantigua H, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Schmidt JM, Lee K, Badjatia N, Agarwal S, et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: who dies, and why? Crit Care 2015;19:309.



21. Mattos JP, Joaquim AF, Almeida JP, Albuquerque LA, Silva EG, Marenco HA, et al. Decompressive craniectomy in massive cerebral infarction. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2010;68:339–345.


22. Mori K, Nakao Y, Yamamoto T, Maeda M. Early external decompressive craniectomy with duroplasty improves functional recovery in patients with massive hemispheric embolic infarction: timing and indication of decompressive surgery for malignant cerebral infarction. Surg Neurol 2004;62:420–429; discussion 429-430.


23. Neugebauer H, Schnabl M, Lule D, Heuschmann PU, Juttler E, Group IS. Attitudes of patients and relatives toward disability and treatment in malignant MCA infarction. Neurocrit Care 2017;26:311–318.


24. Schwab S, Steiner T, Aschoff A, Schwarz S, Steiner HH, Jansen O, et al. Early hemicraniectomy in patients with complete middle cerebral artery infarction. Stroke 1998;29:1888–1893.


25. Stocchetti N, Croci M, Spagnoli D, Gilardoni F, Resta F, Colombo A. Mass volume measurement in severe head injury: accuracy and feasibility of two pragmatic methods. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000;68:14–17.



26. Sundseth J, Sundseth A, Jacobsen EA, Pripp AH, Sorteberg W, Altmann M, et al. Predictors of early in-hospital death after decompressive craniectomy in swollen middle cerebral artery infarction. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2017;159:301–306.


27. Suyama K, Horie N, Hayashi K, Nagata I. Nationwide survey of decompressive hemicraniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction in Japan. World Neurosurg 2014;82:1158–1163.


28. Turkeltaub PE, Messing S, Norise C, Hamilton RH. Are networks for residual language function and recovery consistent across aphasic patients? Neurology 2011;76:1726–1734.



- TOOLS